この記事について
この記事は、2022年9月に実施した社内勉強会の内容をもとに、社外向けに再編集したものです。
記載の内容は当時の知見に基づいており、現在の仕様やベストプラクティスとは異なる場合があります。
実装の際は、最新の公式ドキュメントをご確認ください。
はじめに
本記事では、Railsアプリケーションの開発現場で実際に発生したセキュリティ上の課題と、その対策方法をご紹介します。
実例を通じて、Railsにおけるセキュリティ対策の基本的な考え方を整理しています。
参考:
- TechRacho(hachi8833) – Railsアプリで実際にあった5つのセキュリティ問題と修正方法(翻訳)
https://techracho.bpsinc.jp/hachi8833/2021_10_28/62858 - Railsガイド – Railsセキュリティガイド
https://railsguides.jp/security.html
セッション
アプリケーションはセッションを用いて、多くのユーザーがアプリケーションとやりとりできるようにしつつ、各ユーザー固有のステートを維持します。たとえばセッションを用いることで、ユーザーが認証されれば以後のリクエストでサインインしたままにできます。
引用:Railsセキュリティガイド – 3 セッション – 3.1 セッションとは何か
https://railsguides.jp/security.html
セッションハイジャック
- セッション情報はcookieに保存されています。
- 暗号化されていない通信環境(例:公開Wi-Fi)では、セッション情報が傍受されるリスクがあります。
対策
- SSL(HTTPS)を常に使用し、安全な接続の提供を行う必要があります
- Rails 3.1以降では、アプリケーションの設定ファイルで以下のようにSSL接続を強制できます
config/environments/production.rb
# Force all access to the app over SSL, use Strict-Transport-Security, and use secure cookies.
# config.force_ssl = true※ AWSなどのインフラ側でSSL終端している場合でも、Railsアプリ側の設定はセキュリティヘッダーやcookieに影響するため有効です。
無期限セッション
- 毎回ログインする手間がなくて便利だが、攻撃者に狙われやすくなるリスクもあります
対策
- ログアウトボタンを目立つデザインにしましょう。
- Cookieには有効期限を設定します。(ただし、書き換えが容易なため変更される可能性があります)
config/initializers/session_store.rb
Rails.application.config.session_store :cookie_store, expire_after: 12.hours- セッションの有効期限はサーバー側で管理します。(
gem deviseを使う場合)
# timeoutableモジュールでユーザーセッションの期限切れ検証可能
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
devise :timeoutable
end
config/initilizers/devise.rb
# ==> Configuration for :timeoutable
# The time you want to timeout the user session without activity. After this
# time the user will be asked for credentials again. Default is 30 minutes.
config.timeout_in = 30.minutes
CSRF(クロスサイトリクエストフォージェリ)
Railsでは、CSRF対策としてデフォルトで protect_from_forgery が有効になっています。
不正な外部サイトからのリクエストに備えるため、改めて仕組みや対策を把握しておくと安心です。
参考記事:
- RailsにおけるCSRF対策まとめ(Zenn)
https://zenn.dev/cobachie/articles/rails-security - TechRacho: Railsアプリのセキュリティ対策事例
https://techracho.bpsinc.jp/hachi8833/2021_11_26/46891
ユーザー管理
アカウントロック
サインインの失敗回数に制限がないと、総当たり攻撃や辞書攻撃のリスクが高まり、セキュリティホールとなる可能性があります。
対策
- 一定回数ログインに失敗した場合にアカウントをロックすることで、不正アクセスを防ぎます(
gem deviseを使用する場合)
# lockableモジュールでサインインの試行回数を制御可能
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
devise :lockable
end
config/initilizers/devise.rb
# ==> Configuration for :lockable
# Defines which strategy will be used to lock an account.
# :failed_attempts = Locks an account after a number of failed attempts to sign in.
# :none = No lock strategy. You should handle locking by yourself.
# config.lock_strategy = :failed_attempts
# Defines which key will be used when locking and unlocking an account
# config.unlock_keys = [:email]
# Defines which strategy will be used to unlock an account.
# :email = Sends an unlock link to the user email
# :time = Re-enables login after a certain amount of time (see :unlock_in below)
# :both = Enables both strategies
# :none = No unlock strategy. You should handle unlocking by yourself.
# config.unlock_strategy = :both
# Number of authentication tries before locking an account if lock_strategy
# is failed attempts.
# config.maximum_attempts = 20
# Time interval to unlock the account if :time is enabled as unlock_strategy.
# config.unlock_in = 1.hour
# Warn on the last attempt before the account is locked.
# config.last_attempt_warning = true
ユーザーリスト
「パスワードをリセットする」機能でメールアドレスを入力した際に、
「そのメールアドレスのユーザーは存在しません」といったメッセージを表示してしまうと、
システムに登録されているかどうかを第三者が判別できてしまうリスクがあります。
対策
入力されたメールアドレスが登録済みかどうかに関わらず、同じメッセージを返すようにします。
config/initilizers/devise.rb
# It will change confirmation, password recovery and other workflows
# to behave the same regardless if the e-mail provided was right or wrong.
# Does not affect registerable.
# config.paranoid = true
権限のないリソースへのアクセス
ユーザー自身が管理していないデータやリソースにアクセスできてしまうと、重大な情報漏洩につながる可能性があります。
対策
パラメータを使用する場合は、可能な限りアクセスを絞り込むようにしましょう。
Project.find(params[:id])
↓
current_user.projects.find(params[:id])
弱いパスワード
「password」や「123456」、「1qaz2wsx」などの推測されやすいパスワードは不正アクセスの大きなリスクになります。
参考:NordPass – よく使われているパスワード一覧
https://nordpass.com/most-common-passwords-list/?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=top200passords2021
対策
推測されにくい強力なパスワードを使ってもらうために、パスワードポリシーを導入しましょう。
参考:GitHub – How To: Set up simple password complexity requirements
https://github.com/heartcombo/devise/wiki/How-To:-Set-up-simple-password-complexity-requirements
validate :password_complexity
def password_complexity
return if password.blank? || password =~ /^(?=.*?[A-Z])(?=.*?[a-z])(?=.*?[0-9])(?=.*?[#?!@$%^&*-]).{8,70}$/
errors.add :password, "パスワードの強度が不足しています。パスワードの長さは8〜70文字とし、大文字と小文字と数字と特殊文字をそれぞれ1文字以上含める必要があります。"
endその他
Github
Gemのセキュリティアラート(メールでも通知)
GitHub では、使用している Gem のセキュリティアラートを通知してくれます。(メール通知あり)
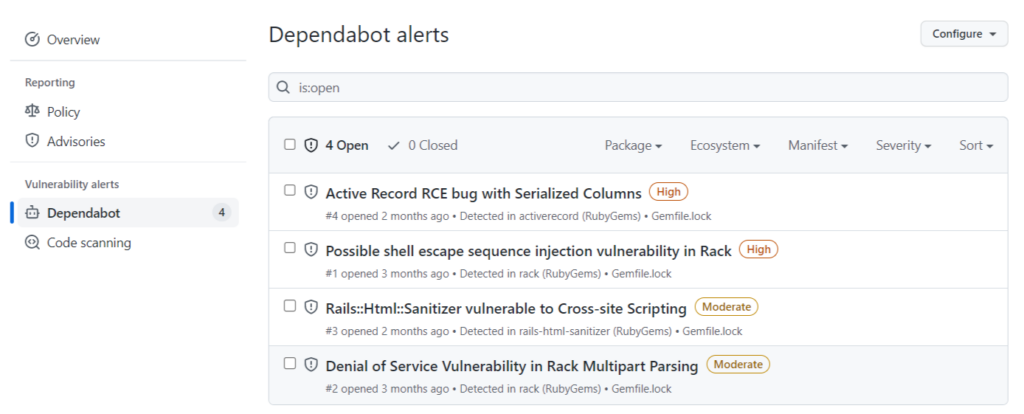
アクセストークンなど機密性の高い情報をコミットしてしまった場合にも、メールで通知してくれます。
オプスインでの対応
Brakeman
Rails アプリケーションのソースコードからセキュリティ上の問題を検出してくれる静的解析ツールです。
参考:TECH BLOG by GMO – gem BrakemanでRails製アプリケーションの脆弱性を検知する
https://techblog.gmo-ap.jp/2021/12/06/rails-brakeman/(参照:2022/09)
gem "brakeman"
$ bundle install
$ brakeman -A
以下のようにconfig.force_ssl が有効になっていない場合など、インフラ側の設定が原因の警告(例: “Missing Encryption”)については、対応は不要です。
High Missing Encryption [311]
The application does not force use of HTTPS: config.force_ssl is not enabled near line 1OWASP
OWASP ZAP は、Webアプリケーション向けの脆弱性スキャンツールです。
参考:アイティーエム – OWASPとは?ZAP、TOP10、Testing Guide、ASVSなどを中心に解説
https://www.itmanage.co.jp/column/about-owasp/(参照:2022/09)
重要度が「High」の項目は原則として対応必須とし、「Medium」や「Low」の項目は内容を確認したうえで対応を判断します。
※ M1 Mac では公式イメージが未対応のため、以下のように Docker でビルドして対応します。
参考:Zenn(yasuaki640) – Docker版OWASP ZAPをM1 Macで動かす
https://zenn.dev/y640/articles/430e99504cd275(参照:2022/09)
git clone https://github.com/zaproxy/zaproxy
cd zaproxy/docker
docker build -f Dockerfile-stable -t yasuaki640/zap2docker-stable-m1 .
// スキャン実行(localhost指定では動作しないのでIP指定する)
docker run -t yasuaki640/zap2docker-stable-m1 zap-baseline.py -t http://192.168.0.104:3100/users/loginCSP関連の警告
CSP(コンテンツセキュリティポリシー)を導入することで、スクリプトインジェクションなどの攻撃を未然に防ぐことができます。以下の2点を設定しましょう。
config/initializers/content_security_policy.rbを有効化application.html.erbにmetaタグ追加
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; img-src https://*; child-src 'none';script-src 'self';">
# プロジェクト独自の対応
<meta http-equiv=“Content-Security-Policy” content=“default-src 'self'; font-src 'self' https://fonts.gstatic.com; img-src 'self' https://code.jquery.com https://s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com; object-src 'none'; script-src 'self'; script-src-attr 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; style-src 'self' https://code.jquery.com https://fonts.googleapis.com; style-src-attr 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; form-action 'self'; frame-ancestors 'none'“>参考サイト
出典: TechRacho(hachi8833) – Railsアプリで実際にあった5つのセキュリティ問題と修正方法(翻訳)
https://techracho.bpsinc.jp/hachi8833/2021_10_28/62858
出典: Railsガイド – Railsセキュリティガイド
https://railsguides.jp/security.html
出典: RailsにおけるCSRF対策まとめ(Zenn)
https://zenn.dev/cobachie/articles/rails-security
出典: TechRacho: Railsアプリのセキュリティ対策事例
https://techracho.bpsinc.jp/hachi8833/2021_11_26/46891
出典: NordPass – よく使われているパスワード一覧
https://nordpass.com/most-common-passwords-list/?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=top200passords2021
出典: GitHub – How To: Set up simple password complexity requirements
https://github.com/heartcombo/devise/wiki/How-To:-Set-up-simple-password-complexity-requirements
出典: TECH BLOG by GMO – gem BrakemanでRails製アプリケーションの脆弱性を検知する
https://techblog.gmo-ap.jp/2021/12/06/rails-brakeman/
出典: アイティーエム – OWASPとは?ZAP、TOP10、Testing Guide、ASVSなどを中心に解説
https://www.itmanage.co.jp/column/about-owasp/
出典: Zenn(yasuaki640) – Docker版OWASP ZAPをM1 Macで動かす
https://zenn.dev/y640/articles/430e99504cd275
出典: Railsガイド – CSPセクション
https://railsguides.jp/security.html#content-security-policy